Cybersecurity For Startups: A Step-by-Step Guide
With cybercrime costs projected to hit $10.5 trillion annually from 2025, startups cannot afford to be complacent. A single breach can derail operations, shake investor confidence, and stunt growth. However, with the right approach, these risks can be effectively managed. By embedding security into your core operations, you can protect your startup while positioning it for growth, trust, and long-term success.
This guide provides simple, cost-effective cybersecurity tips for startups to protect your business. Read on to safeguard what you’ve built and gain a competitive edge.
Why Cybersecurity is Important for Startups?
Startups drive innovation, but security often gets overlooked in a rush to grow. This can lead to severe consequences. A single data breach could expose customer information, proprietary technology, or financial records, damaging reputation and finances.
Beyond financial losses, cybersecurity is critical for meeting regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Non-compliance can mean steep fines and legal troubles, which many startups can’t afford. On the positive side, investing in cybersecurity builds trust with customers, investors, and partners, showing your commitment to protecting data and maintaining integrity.
Why Cyberattacks Often Target Startups?
Cybercriminals often target startups because they handle valuable data and are connected to larger organizations. They hold sensitive information such as customer data, proprietary technology, and intellectual property but often lack the advanced security measures of larger companies. Limited budgets mean they can only afford basic protections, like outdated software or weak firewalls, which leave them more vulnerable to attacks.
Addressing these potential risks and implementing cybersecurity best practices for businesses that are exposed can help protect their data.
What Challenges Do Startups Face When It Comes to Cyber Threats?
Cybersecurity for startups faces various challenges that include:
- Limited Resources
Nearly 46% of cyber breaches target businesses with fewer than 1,000 employees, and one reason is tight budgets. Startups often rely on basic tools like antivirus software or default cloud settings, which provide only limited protection. These gaps make it easier for attackers to exploit security vulnerabilities with advanced threats like phishing or ransomware.
- Rapid Scaling
The rapid growth of startups often creates vulnerabilities in their infrastructure. Developers under tight deadlines may leave APIs unsecured, and misconfigured cloud environments can provide attackers with easy access. For example, a poorly managed CI/CD pipeline during a product launch could expose sensitive code repositories. To keep up with demand, startups often skip thorough security audits, further increasing their risk.
- Data Sensitivity
Startups handle valuable data, including customer PII (e.g., names, emails, financial details) and proprietary business information like trade secrets or patents. This makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals. For startups in industries like fintech or healthcare, this stolen data can result in direct financial losses and operational disruption. In 2023, over 353 million individuals were affected by data compromises, including breaches, leakage, and exposure in the US alone.
- Targeted Attacks
Cybercriminals often view startups as easy targets for Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)—long-term attacks designed to steal valuable data or disrupt operations. These attacks are strategically timed to cause maximum damage, such as during startup funding rounds or major product launches. Lacking strong monitoring and defense systems, startups often fail to detect these threats until it’s too late.
- Employee Behavior
Human error accounts for over 74% of cybersecurity incidents, making it a major vulnerability for startups. Employees may use weak passwords, fall victim to phishing scams, or access work systems on unsecured networks. For example, an untrained employee might click on a convincing spear-phishing email, exposing sensitive company data.
- Cloud Vulnerabilities
SaaS Startups often depend on cloud services to store and manage data, but misconfigured settings and weak access controls can leave sensitive information exposed. For example, 31% of S3 buckets are publicly accessible, making them vulnerable to unauthorized access, data leaks, and attacks.
Similarly, a misstep configuring Microsoft Azure’s Blob Storage once exposed sensitive data from over 65,000 companies across 111 countries. These examples highlight how even minor oversights can have major consequences. Without the expertise to implement advanced cloud security requirements, startups become easy targets for ransomware attacks and other threats.
- BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) Policies
To cut costs, startups often let employees use personal devices for work through Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies. However, these devices often lack strong security and may connect to unsecured networks, creating vulnerabilities.
Startups can address these risks with tools like Mobile Device Management (MDM) and practices such as enforcing strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA), and using secure VPNs. Additional steps like separating work data from personal apps, verifying device security, and limiting access based on location or behavior further enhance protection.
- Reputation Risk
A security breach can be devastating for a startup’s reputation beyond the immediate financial loss. Customers expect their data to be secure, and a single incident can lead to bad press, loss of trust, and investor hesitation. For example, small businesses in Australia lose an average of $50,000 per cyber incident, but the reputational damage often costs even more. Startups that rely on credibility for growth may struggle to recover from such a breach.
- Supply Chain Risks
Startups rely on third-party vendors, tools, and integrations to scale quickly. While efficient, this creates vulnerabilities in the supply chain. An attacker may target a less secure vendor to gain access to the startup’s systems or even those of its partners. For instance, the SolarWinds breach demonstrated how a single compromised vendor could lead to widespread damage across an ecosystem.
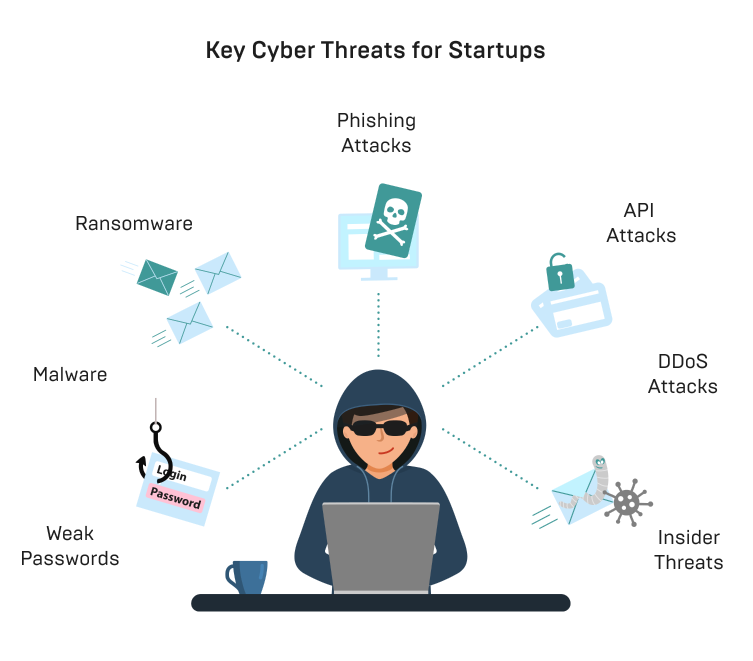
Key Cyber Threats Startups Are Likely to Encounter
Below are the major threats that can disrupt operations, harm reputations, and drain startup resources.
- Phishing Attacks
Phishing tricks employees into sharing sensitive information like passwords or financial details. Startups are especially vulnerable because they often lack security training. These attacks can quickly disrupt operations during busy times like launches or funding rounds.
- Ransomware
Ransomware locks up important files and demands payment to release them, often threatening to leak stolen data. Startups, especially those without strong backup systems, struggle to recover quickly, leading to financial and reputational damage.
- Insider Threats
Insider threats happen when employees or contractors, either accidentally or on purpose, compromise security. Startups are at risk because they often lack strict access controls and fail to remove former employees’ credentials.
- Malware
Malicious software sneaks into systems through unverified downloads or compromised tools. Startups relying on open-source software can easily fall victim. This type of attack not only affects the startup but can harm clients and partners, too.
- Data Breaches and Cloud Security Risks
Data breaches often result from misconfigured cloud storage or weak access controls. Startups using pre-configured cloud services without regular audits are especially vulnerable. These breaches can lead to fines, lost customers, and damaged reputations.
- Cloud Security Risks
Cloud services make it easy for startups to scale quickly, but misconfigurations or weak permissions are common issues. Without regular audits or security tools, sensitive information stored in the cloud can be exposed, making it an easy target for attackers.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks overwhelm systems with fake traffic, causing them to crash. Startups, especially during launches or high-traffic periods, often lack the infrastructure to handle such attacks, leading to downtime and lost revenue.
- Weak Passwords
Weak or reused passwords make it easy for attackers to break into accounts. Startups often prioritize convenience over security, and without Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), a single compromised password can expose critical systems.
- IoT Device Vulnerabilities
IoT devices like cameras or sensors often have weak security settings. Startups that don’t change default passwords or update device software risk letting attackers access their broader network.
- API Threats
APIs allow startups to connect with third-party tools, but they can be a weak point if not secured properly. Poor authentication or data validation can let attackers exploit these endpoints to steal information or disrupt services.
How Much Do Companies Spend on Cybersecurity?

new cybercecurity
Startups typically allocate around 10-13% of their IT budgets to cybersecurity, with smaller companies sometimes dedicating up to 22.7% depending on their size, industry, and level of risk. This includes expenses for tools like firewalls and endpoint protection, outsourced security services, and compliance with regulations such as PCI DSS or HIPAA. Cybersecurity for startups in high-risk sectors, like fintech or health tech, may require an even higher percentage to secure sensitive data and meet strict regulatory requirements.
Striking the Right Balance
Underinvesting in cybersecurity can have devastating consequences. According to IBM, the average cost of a data breach is $4.24 million, but the stakes are even higher for startups. To avoid any losses, startups should focus their budgets on high-impact, scalable solutions such as employee training, robust password policies, and basic monitoring tools, ensuring they build a secure foundation without overspending.
What Services Do Cybersecurity Companies Provide?
Here’s a closer look at the key services a cybersecurity company may offer startups:
- Threat Detection and Monitoring
Startups often lack 24/7 system monitoring. Cybersecurity companies use tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS) to track threats in real-time, catching vulnerabilities before they escalate. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and prevents reputational damage.
- Vulnerability Assessments
Startups scaling quickly can leave security gaps, like unprotected APIs or outdated software. Vulnerability assessments uncover these weaknesses and prioritize fixes, helping startups secure their operations without disrupting growth.
- Incident Response and Recovery
A single breach can derail a startup. Cybersecurity providers create tailored incident response plans to contain threats, mitigate damage, and restore operations quickly. This is vital for startups handling sensitive data in industries like fintech or healthcare.
- Managed Security Services
Managed services, including firewall management and endpoint protection, offer scalable security solutions for startups without in-house IT teams. This lets startups focus on growth while maintaining strong defenses on a budget.
- Compliance Support
Startups in regulated sectors like healthcare or fintech face strict requirements such as HIPAA or GDPR. Cybersecurity companies provide audits and system optimization to ensure compliance, build customer trust, and avoid fines.
- Employee Training and Awareness
Human error is a common vulnerability. Cybersecurity providers train employees to recognize phishing attempts and handle data securely, promoting a culture of security that emphasizes preventive measures.
- Integrated Cybersecurity Strategy for Startups
These services work together to build a comprehensive defense. For example, vulnerability assessments identify risks that threat monitoring systems track, while training reinforces compliance policies. This holistic approach ensures startups can scale securely.
Over To You
Security for startups looking to grow safely and build trust is a must. To stay safe, follow the cybersecurity tips for small businesses highlighted in this article, which include training your team and securing access points to be safe.
If you are building apps or using cloud solutions, consider partnering with reliable software development companies that prioritize security. For instance, Reenbit integrates security into every stage of software development for startups, from custom software to cloud engineering and digital transformation. With us, you can focus on innovation, knowing your platform is secure, scalable, and built to last.