How the Retail Industry Uses Business Intelligence for Growth
Retail is a high-speed, high-stakes business. Margins are tight, demand shifts fast, and yesterday’s instincts no longer cut it. Growth now depends on clarity, and that’s where Business Intelligence (BI) steps in.
BI gives retailers a clearer view of their business. It connects sales, inventory, customer behavior, and supply chain systems into one clear picture, delivering real-time insights retailers can act on. The result? Faster decisions, leaner operations, more innovative promotions, and stronger customer loyalty. And numbers back it up: according to Deloitte, companies with data-driven CEOs are 77% more likely to succeed.
This article explains how leading retailers apply BI: the systems they connect, the challenges they solve, and the results they see. Continue reading to learn more!
What is Business Intelligence in Retail?
Business intelligence (BI) in retail is the strategic process of turning data into a competitive advantage. It combines information from across the business, including sales, inventory, customer interactions, and supply chains, and applies advanced analytics to reveal hidden patterns, trends, and opportunities.
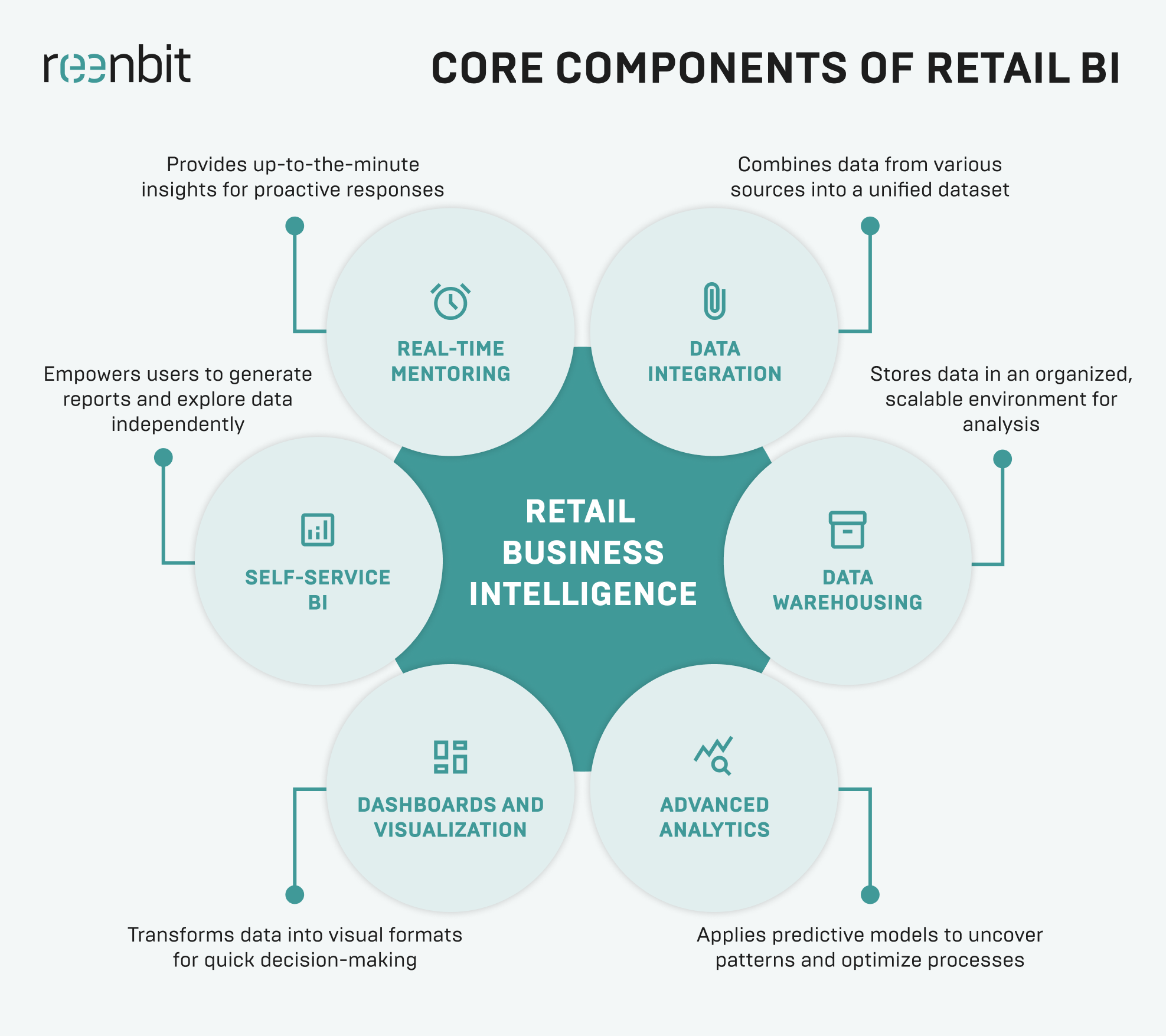
Key Components of Retail BI
An effective retail business intelligence solution integrates several core components:
- Data Integration: Combines data from point-of-sale (POS) systems, e-commerce platforms, CRM databases, ERP software, and supply chain systems into a centralized, cohesive dataset..
- Data Warehousing: Stores integrated data in an organized, scalable environment that supports efficient querying and long-term analysis.
- Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning: Applies predictive models to uncover demand patterns, forecast sales, optimize inventory, and personalize customer experiences.
- Dashboards and Visualization Tools: Turn raw data into charts, heatmaps, and trend lines that store managers, marketers, and executives can use to make fast, informed calls.
- Self-Service BI: Empowers business users—without technical expertise—to generate reports, explore data, and test scenarios independently.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Delivers up-to-the-minute insights and alerts, allowing business owners to respond proactively to changes in sales trends, customer behavior, or supply chain dynamics.
These components provide data visibility and the strategic insight necessary for growth, efficiency, and competitive differentiation.
What Are the Key Benefits of Retail Business Intelligence?
Today’s retail world moves fast. Retailers need more than data to keep up; they need clear, timely actionable insights, and business intelligence makes this possible. Here’s how BI delivers real value.
Smarter Decisions
Good decisions depend on good timing. BI gives retailers the visibility to act while conditions are still shifting, not after the fact. In one 2024 study, companies using real-time analytics cut decision-making time by 30%, giving them a critical speed advantage when responding to market shifts or sudden changes in customer behavior.
Better Inventory Management
Poor inventory planning eats into margins, whether it’s excess stock sitting idle or products selling out too soon. BI helps retailers strike the right balance. According to recent research, 73% of retailers using forecasting tools improved inventory accuracy, reducing both overstock and stockouts. With real-time visibility into turnover, BI allows teams to adjust ordering, transfer stock between locations, and stay aligned with demand as it evolves.
Higher Sales and Revenue
Business Intelligence tools empower retailers to identify sales trends and customer preferences, leading to increased revenue. According to Forrester Research, retailers implementing comprehensive BI solutions report an average 8.4% increase in sales volume within the first year of adoption.
By analyzing customer data, retailers can tailor offerings and promotions to boost sales. BI tools help pinpoint which products are driving revenue, which ones are lagging, and how pricing changes affect demand. With this visibility, retailers can adjust pricing and promotions to drive results where they matter most.
Personalized Customer Experiences
Personalized experiences drive customer loyalty and sales. McKinsey reports that 71% of consumers expect personalized experiences, and 76% get frustrated when they don’t receive them. BI turns customer data into detailed behavioral patterns, so retailers can tailor recommendations, trigger timely offers, and engage each shopper in relevant ways—at scale.
Lower Operational Costs
Many retailers waste money without realizing it, whether it’s through bloated staffing, excess freight, or poor stock rotation. BI helps surface those inefficiencies. In fact, Deloitte found that companies using BI for operational decisions cut costs by over 14.2% within three years. That value comes from smarter scheduling, leaner warehousing, and eliminating spend on what isn’t driving results.
By analyzing customer data, retailers can tailor offerings and promotions to boost sales. BI tools help pinpoint which products are driving revenue, which ones are lagging, and how pricing changes affect demand. With this visibility, retailers can adjust pricing and promotions to drive results where they matter most.
Real-Time Monitoring
In retail, waiting even a day to act on data can mean missed revenue or lost customers. That’s why real-time monitoring is becoming standard. By 2025, 70% of organizations are expected to use real-time analytics, nearly double the number from just a few years ago. BI enables teams to monitor sales, supply chain bottlenecks, or marketing performance as it happens, not in hindsight.
Core Use Cases of Business Intelligence in Retail
Business intelligence for retail has moved beyond reporting—it now drives decision-making across every layer of retail. Leading brands collect data and turn it into strategic insights that fuel growth, improve customer experiences, and sharpen operational efficiency. Here’s how the most competitive retailers are using BI today.
Sales Performance Tracking
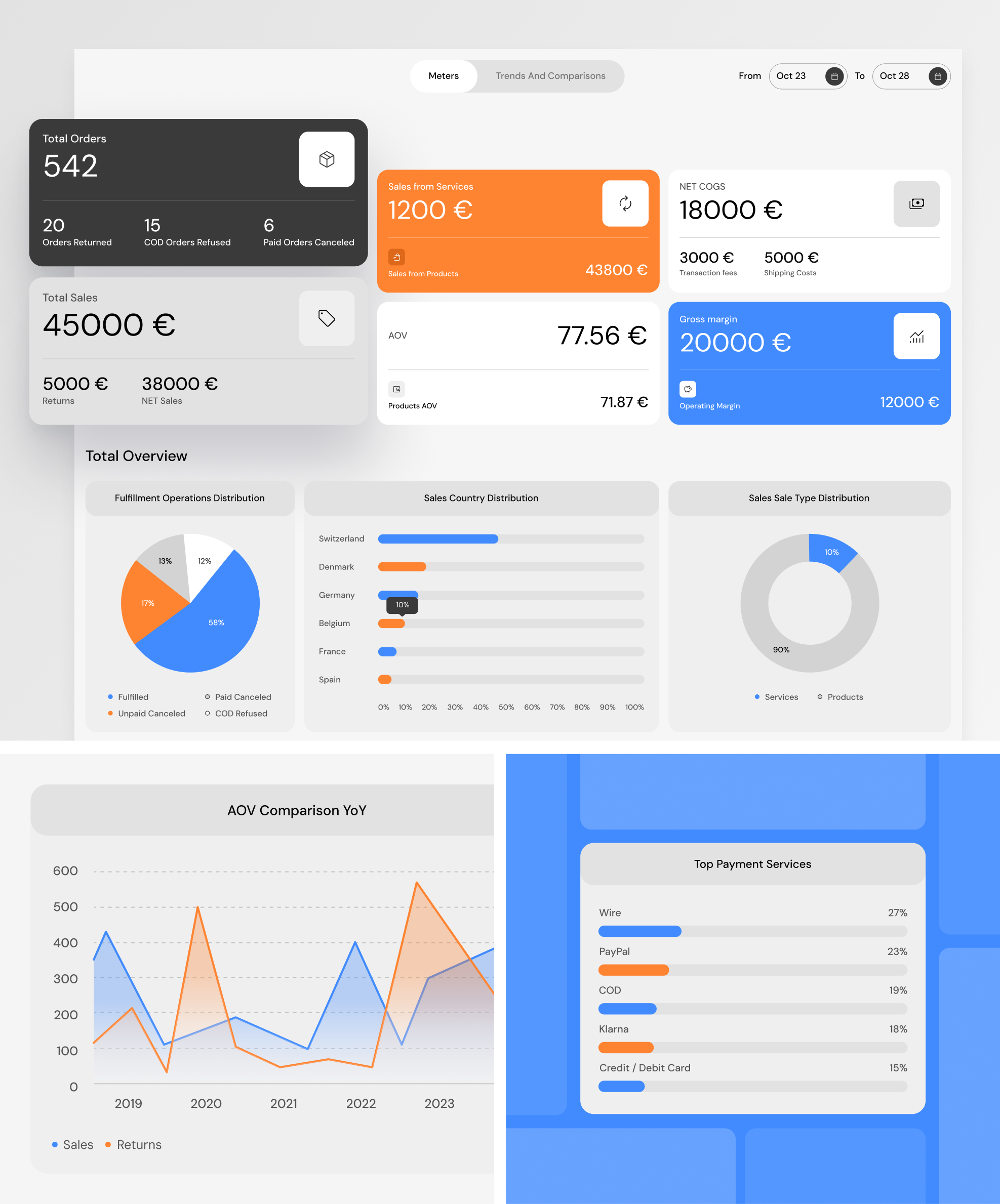
In retail, timing is everything. BI empowers companies to monitor real-time sales data, spot emerging trends, and measure how products, promotions, and sales channels perform. With this visibility, retailers can pull slow-moving products faster and double down on what’s gaining traction before competitors even notice the shift.
Top retailers now integrate POS data, e-commerce metrics, and third-party marketplace performance into unified dashboards. This allows not just historical tracking but near-instant feedback loops. For example, dynamic pricing or targeted digital marketing can address a mid-promotion sales lag. According to McKinsey, data-driven retailers are 23 times more likely to outperform competitors in acquiring customers and 19 times more likely to achieve profitability.
Inventory Tracking with Demand Forecasts
Overstocking ties up capital and increases holding costs. On the other hand, stockouts lead to lost revenue and damaged customer trust. BI systems combine historical sales data with factors like seasonality, regional trends, and weather forecasts to improve the accuracy of demand prediction.
Industry leaders now use AI-enhanced demand forecasting tools that dynamically adjust inventory targets across locations. As a result, many have significantly reduced stockouts while maintaining leaner inventory levels. Research from McKinsey indicates that advanced analytics in inventory management can improve forecasting accuracy by up to 65%, driving meaningful gains in both sales and operational efficiency.
Customer Behavior Analysis
Modern BI doesn’t just reveal what customers buy—it explains why. By connecting loyalty program data, website interactions, and purchase history, BI helps retailers uncover patterns that predict future buying behaviors. This allows marketing teams to personalize offers and tailor customer engagement at scale.
Retailers leveraging data-driven personalization have reported sales conversion lifts of 10–15%, with some sectors achieving even higher improvements. BI systems also support testing and refining engagement strategies, ensuring personalization evolves alongside customer expectations and market changes.
Pricing Optimization
Pricing is both a science and an art, but BI is shifting the balance toward science. Retailers can now analyze competitor pricing, demand elasticity, inventory levels, and customer purchasing patterns to optimize prices dynamically. This means moving beyond periodic price reviews to real-time price adjustments based on live market and customer data.
Dynamic pricing is no longer confined to e-commerce giants. Today, even mid-sized retailers adopt algorithmic pricing models, often seeing modest but measurable revenue improvements. While specific uplift percentages vary widely, studies consistently point to better margins and improved sell-through rates for companies that adopt data-driven pricing strategies.
Store and Location Performance Analytics
No two stores—or customer demographics—perform identically. BI tools enable retailers to evaluate location-specific sales, foot traffic patterns, and local market trends. This data informs smarter decisions about product assortment, store layouts, and staffing.
Advanced BI platforms now pull in POS data, geospatial analytics, and socio-economic indicators to build a 360-degree view of store performance. This allows underperforming locations to be adjusted proactively and high-performing formats to be replicated. Research by Forrester highlights that data-driven store planning can increase overall retail space productivity by up to 12%.
Now that you know the benefits of business intelligence in the retail industry, let’s explore its applications today.
Real-World Examples of Retail BI in Action
How would the retail industry use business intelligence? These real-world examples show how leading brands apply BI to streamline operations, reduce waste, and drive growth.
1. Building a Unified Data Ecosystem for a Fashion Retailer
A Swiss fashion brand partnered with Reenbit to unify fragmented data from Shopify, PrestaShop, and multiple courier systems. Manual reporting slowed decision-making, so the goal was to build an automated pipeline that delivered real-time visibility into financial and operational performance.
The team faced early roadblocks—Shopify’s GraphQL API lacked native Azure Data Factory support, and sensitive data required secure integration. Reenbit engineered a robust solution using Azure Data Factory, SQL Server, and KeyVault, with Power BI dashboards layered on top. The result? Manual reporting time was cut in half, and the retailer gained always-on access to key business metrics, all with a scalable, cloud-native stack.
2. Gaining Real-Time Insights into Product Performance
Another boutique fashion brand, working with Woven Insights, introduced BI dashboards to track new collection launches across channels. Before the rollout, the team relied on delayed reports and gut instinct to manage stock decisions.
The shift came quickly. Within days of launch, the BI dashboard revealed a sharp sales spike in specific color variants, while others lagged behind. Instead of waiting weeks for manual sales reports, the team used real-time data to reorder fast-selling items and promote the slow movers, avoiding both stock-outs and dead stock. It was a small change with a big effect: tighter inventory cycles and quicker reaction to customer demand.
3. Reducing Waste Through Smarter Grocery Analytics
Walmart, Kroger, and other major grocers use Crisp’s Retailer Waste dashboard to combat one of their biggest challenges: excess product waste. The platform consolidates data from shipments, POS systems, and inventory counts to identify losses from spoilage, miscounts, or shrinkage.
For example, if a store receives 100 units but can only reconcile 70 through sales and stock levels, BI surfaces the 30 missing units and helps isolate where the breakdown occurred. The dashboard’s layered views—Overview, Drivers, and Details—let teams drill down to identify whether the issue lies with supplier deliveries, in-store handling, or inaccurate counts.
4. Personalizing Offers in Real Time at Scale
Bol.com, one of the largest e-commerce platforms in the Netherlands and Belgium, took personalization to the next level with near real-time customer feed updates. The system fine-tuned recommendations as users browsed by refreshing embeddings every two minutes and calculating product similarity scores.
Unlike static “recently viewed” lists, this approach responded to live user behavior, serving highly relevant promotions that evolved with each session. The strategy paid off: Bol.com recorded a 4.9% increase in conversions, proving that precision timing in personalization translates directly to revenue impact.
Integrating BI with Retail Systems
For BI to deliver real results, it has to connect directly with retail operations systems, pulling clean, timely data from inventory, customer, and sales platforms into a single source of truth. Let’s explore the available integration options.
ERP and Inventory Systems
Integrated BI dashboards let retailers move beyond passive ERP reporting. They can track real-time stockouts across locations, visualize aging inventory by SKU, and spot anomalies like mismatched supplier deliveries or margin loss from deadstock. One leading fashion group with multiple brands recently synchronized its ERP, CRM, and accounting systems to enable unified reporting and data visibility across the business—see Reenbit success story.
CRM and Customer Data
With BI layered over CRM data, marketing and sales teams can map entire customer lifecycles—from first purchase to loyalty drop-off. They can compare segments, measure retention rates by channel, and predict churn before it happens. Tools like Salesforce or HubSpot become far more powerful when BI shows not just who your customers are, but what they’re likely to do next.
POS and Real-Time Sales Insights
BI integration with POS systems like Square, Lightspeed, or Oracle Retail unlocks instant visibility into what’s selling, where, and when. Retailers can catch underperforming promotions mid-campaign, spot sudden demand spikes by location, and adjust stock flows dynamically. It’s not just about reporting past sales—it’s about reacting in real time to what’s happening on the floor.
Challenges Retailers Face When Implementing BI
Adopting business intelligence in the retail industry isn’t just about choosing the right dashboard tool. It’s about navigating deep structural challenges that affect data quality, usability, and impact. Here are the most common roadblocks retailers encounter.
- Fragmented Systems, Fragmented Insights
Retailers operate across ERP, CRM, POS, e-commerce, and supplier platforms, each with its own schema, latency, and ownership. BI outputs remain siloed and inconsistent without a unified data model, limiting trust and usability.
- Data Quality Without Accountability
Inaccurate SKUs, inconsistent hierarchies, and untracked adjustments quietly erode BI reliability. Most retailers underestimate how poor data hygiene distorts insights, and few assign ownership to fixing it.
- Lagging Behind the Business
In fast-moving categories like fashion or grocery, batch data pipelines and delayed refreshes make “insights” obsolete when teams see them. Real-time action demands real-time data, but infrastructure often can’t keep up.
- Dashboards That Don’t Drive Action
If BI isn’t embedded in daily decision flows, it becomes background noise. Too many dashboards are designed for analysts, not frontline users. Adoption fails not because of complexity, but because the value is not immediate or clear.
- Scaling Pain—Technically and Commercially
As use cases expand, some BI stacks hit scaling limits—technically (query latency, concurrency) and commercially (licensing, compute costs). Without a future-proof architecture, early wins can stall out fast.
Conclusion
In retail, speed and precision win. Business Intelligence is no longer a support function, it’s infrastructure. BI becomes the engine for real-time decision-making, accurate forecasting, and continuous optimization when integrated across ERP, CRM, POS, and supply chain systems.
The retail companies pulling ahead are those treating BI as core architecture, not an add-on. But delivering that level of intelligence requires more than off-the-shelf tools, it demands technical depth and domain focus.
Reenbit provides both. With specialized Business Intelligence Services and proven expertise in Retail Software Development, Reenbit builds tailored solutions that unify data, eliminate silos, and surface the insights that drive action. The result: stronger margins, faster cycles, and retail teams that don’t just react—they lead.
Ready to turn your data into decisions? Contact us!
FAQ
How is retail business intelligence different from traditional analytics?
Traditional analytics is backward-looking and often manual. Retail BI delivers real-time, connected insights across systems, supporting faster decisions with predictive models, automation, and dynamic dashboards.
What types of data are most useful for retail BI?
BI pulls from POS data, inventory systems, CRM, e-commerce platforms, and external sources like weather or competitor pricing. This combination offers a complete view of operations and customer behavior.
Which metrics should retailers track with BI?
Key metrics include sales by channel, inventory turnover, stockouts, customer lifetime value, promotion performance, and store profitability, all aligned to growth and efficiency goals.
How does BI help improve inventory and supply chain decisions?
BI in the retail industry enables accurate demand forecasting, tracks supplier performance, and flags overstock or stockouts early, helping retailers optimize replenishment and respond to disruptions faster.
Can business intelligence boost sales performance?
Yes. BI reveals what’s driving conversions, highlights product trends, and powers personalized offers—often leading to 5–15% increases in sales performance.
Which BI tools are most commonly used in the retail industry?
Popular tools include Power BI, Tableau, Looker, Qlik Sense, and Google Data Studio, which are often paired with platforms like Azure or Snowflake for data storage and processing.
Is business intelligence suitable for small and mid-sized retailers?
Yes. Cloud BI tools are scalable and accessible, even for lean teams. Retailers can start with key reports and grow into real-time insights as needs evolve.