How to Successfully Implement Business Intelligence in Your Organization
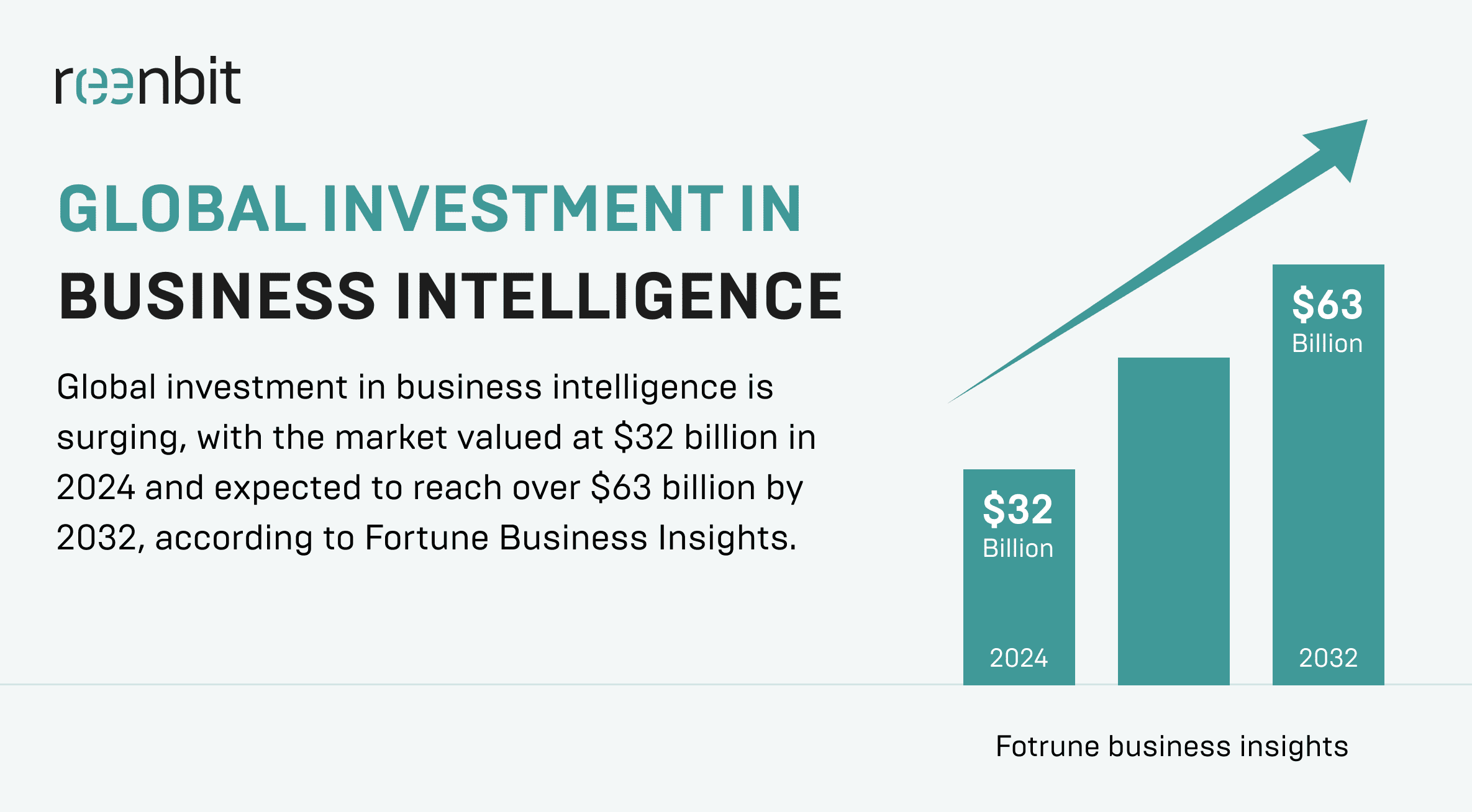
Global investment in business intelligence is surging, with the market valued at $32 billion in 2024 and expected to reach over $63 billion by 2032, according to Fortune Business Insights. However, while adoption rates are rising, success is not necessarily following. Industry data shows that up to 85% of BI initiatives fail to deliver usable insights or reach full deployment.
This disconnect reveals a hard truth: BI failures rarely stem from poor tools; they stem from poor implementation. From misaligned goals to unreliable data foundations and low user adoption, the gap between dashboards and decisions is wider than most leaders expect.
This guide outlines the steps to effectively set up a BI implementation roadmap, from establishing the right strategy to building trust in the data, so your organization achieves tangible results.
What Is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business Intelligence is the strategic use of data to drive better business decisions. It encompasses a set of tools, technologies, and practices that collect, integrate, and analyze information from across an organization, turning fragmented data into clear, actionable insights.
At its core, BI is about visibility. It brings together data from systems such as CRMs, ERPs, and financial platforms into a single, cohesive view, enabling leaders to monitor performance, identify trends, and respond to change with confidence.
Today’s BI platforms go far beyond static reporting. They power real-time interactive dashboards, predictive analytics, and interactive visualizations, helping businesses not only understand what’s happening but anticipate what comes next.
Why Is Business Intelligence Important for Your Organization?
Most businesses today make critical decisions based on outdated reports, siloed data, or incomplete insights. BI matters because it:
- Unifies data across departments to reduce misalignment
- Provides live operational visibility, not static reports
- Replaces gut instinct with evidence-based decisions
- Builds a foundation for a data-driven culture
Now, let’s explore what happens when BI is implemented the right way.
Benefits of Business Intelligence Implementation
Here’s what organizations typically unlock when they move from BI theory to execution:
Faster Decision-Making
BI shrinks time-to-insight. Instead of waiting for static reports, leaders gain real-time visibility into metrics that matter, such as sales velocity, operational bottlenecks, and financial deviations. Decisions become proactive, not reactive.
A Single Source of Truth
Disjointed systems often produce conflicting numbers. BI unifies them into one governed dataset. This alignment eliminates reporting conflicts, speeds up analysis, and ensures every team operates from the same reality.
Improved Forecasting Accuracy
Accurate forecasts require more than historical averages. BI enhances planning by incorporating external variables and predictive modeling. This enables more precise demand projections, more informed resource allocation, and more confident long-term strategies.
Key Steps in Business Intelligence Implementation
While every organization’s path will differ, the following business intelligence implementation steps reflect a proven framework used by successful BI projects across industries.
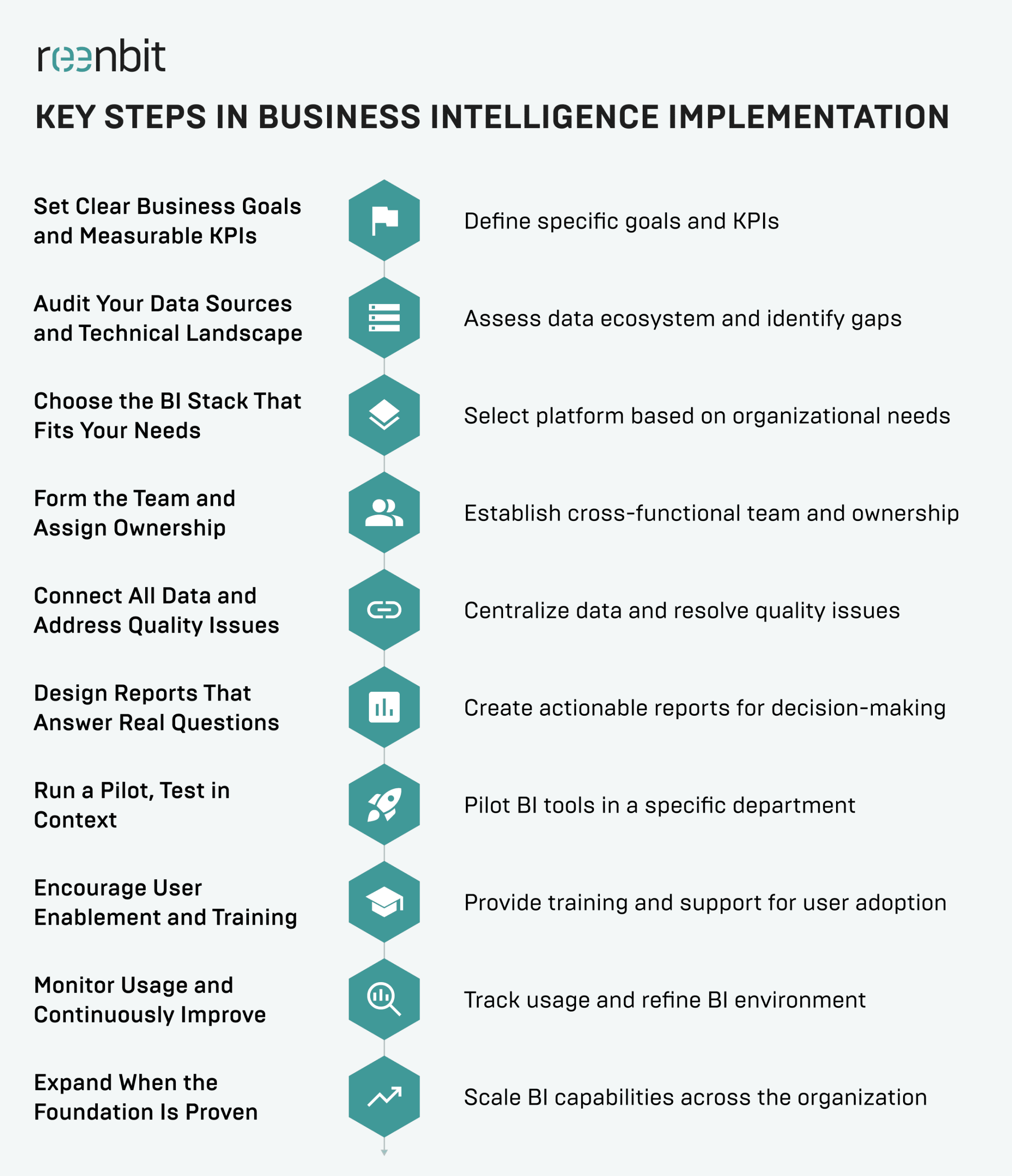
Step 1: Set Clear Business Goals and Measurable KPIs
It’s advisable to begin with clarity on what the business hopes to achieve. Rather than starting with tools, organizations often benefit from defining specific goals such as improving margin visibility, reducing churn, or optimizing resource allocation, and linking them to measurable KPIs. This alignment ensures that BI efforts stay focused on business outcomes rather than technical complexity.
Step 2: Audit Your Data Sources and Technical Landscape
Before selecting platforms or building reports, it’s worth taking stock of the data ecosystem. Where does critical information currently reside? Which systems are in use (ERP, CRM, spreadsheets, cloud platforms), and how accessible and reliable is that data?
A thoughtful audit can reveal integration gaps and potential data silos. These are common challenges in industries like retail, where POS, logistics, and eCommerce platforms often operate independently.
Step 3: Choose the BI Stack That Fits Your Needs
It’s advisable to begin with clarity on what the business hopes to achieve. Rather than starting with tools, organizations often benefit from defining specific goals such as improving margin visibility, reducing churn, or optimizing resource allocation, and linking them to measurable KPIs. This alignment ensures that BI efforts stay focused on business outcomes rather than technical complexity.
Tip: Gartner’s 2024 Magic Quadrant recommends leaders such as Microsoft, Tableau, Looker, Qlik, Oracle, and ThoughtSpot for striking the right balance between usability, governance, and AI-powered business analytics.
Step 4: Form the Team and Assign Ownership
BI succeeds when there’s cross-functional involvement, from IT and data specialists to department heads. Assigning ownership for data governance, development, and enablement ensures that data quality and usability don’t fall through the cracks. It may also be helpful to establish internal BI champions: individuals who bridge the gap between business needs and technical execution.
Step 5: Connect All Data and Address Quality Issues
Bringing data into a centralized warehouse or data lake often reveals inconsistencies (missing fields, duplicates, or conflicting formats) that can compromise trust in insights. Addressing these early through validation, deduplication, and enrichment is essential for reliable analytics. In 2024 alone, about 64% of organizations cited data quality as their top integrity challenge, with duplicate records affecting up to 60% of customer datasets.
Step 6: Design Reports That Answer Real Questions
Rather than flooding teams with dashboards, focus on reports that support real decisions, such as margin erosion alerts, fulfillment delays, or cross-channel marketing ROI. As a guiding principle: if a report doesn’t inform action, it may not be worth building.
Step 7: Run a Pilot, Test in Context
Before rolling out BI company-wide, piloting within a single department, such as sales, finance, or operations, can reveal how tools perform in a real-world setting. Pilots help validate technical assumptions, uncover gaps in data readiness, and surface feedback from actual users. Just as importantly, they generate early proof points that build momentum for broader adoption.
Step 8: Encourage User Enablement and Training
No BI system drives value if people don’t use it. Adoption grows when teams see relevance to their day-to-day work. However, that requires more than documentation; it needs hands-on sessions, role-specific dashboards, and peer-driven support. Many organizations benefit from lightweight programs such as “BI office hours” or internal champions who can answer questions and promote best practices within teams.
Step 9: Monitor Usage and Continuously Improve
Monitoring how dashboards are used, which reports drive decisions, and where friction arises helps BI teams iterate effectively. What’s ignored can be retired. What’s overused may need refinement. Treat the environment as a living product that is responsive to feedback and business change.
Step 10: Expand When the Foundation Is Proven
Once BI begins delivering value, such as reducing reporting overhead, improving forecasting, or surfacing insights that drive change, it often makes sense to scale. This might include onboarding new departments, expanding data coverage, or introducing advanced capabilities such as scenario modeling or machine learning. However, expansion works best when it builds on what is already working.
Now that the BI implementation steps are clear, let’s look at the potential pitfalls.
Common BI Implementation Challenges
When foundational issues go unaddressed, even well-resourced BI initiatives can fall short. Here are five challenges that consistently undermine business intelligence projects:
Unclear Business Objectives
When BI projects commence without a clear definition of success, they often yield dashboards that appear visually appealing but serve no practical purpose. Misaligned goals lead to scattered metrics, low engagement, and confusion about what decisions BI is meant to support.
Data Silos and Integration Issues
Disparate systems (such as ERP, finance, eCommerce, and CRM systems) often store critical data in incompatible formats or under separate governance rules. Without thoughtful data integration, BI efforts risk reflecting only part of the truth.
Bad or Incomplete Data
Poor data quality silently erodes trust. Incomplete fields, outdated records, or inconsistent naming conventions can render even the most elegant dashboards useless. More critically, once trust is broken, users tend to disengage entirely.
Low User Adoption
Lack of adoption is rarely a tooling issue. It’s usually a sign that users don’t see value, don’t trust the data, or don’t understand how BI fits into their role. Without active enablement (training, role-based access, and iterative feedback loops), BI becomes shelfware.
Lack of Internal Expertise
Many BI projects struggle simply because no one owns them internally. A lack of experienced analysts, architects, or product owners can stall momentum and lead to a dependence on external consultants.
Business Intelligence Implementation Costs
The cost of implementing business intelligence varies significantly based on scale, complexity, and organizational maturity. Mid-sized deployments typically range from $10,000 to $100,000, while enterprise initiatives, especially those involving data modernization or AI integration, can exceed $1 million.
But rather than fixate on platform pricing, it’s more effective to understand where the costs lie and why they matter.
Software Licensing and Platform Fees
Most BI tools follow a subscription model. Entry-level licenses (e.g., Power BI Pro) typically start at $250 per user annually, but this cost increases significantly with advanced analytics, AI features, or enterprise-grade governance. Tools like Tableau, Looker, and Qlik are often priced based on usage tiers or organizational size, making scalability a core consideration.
Infrastructure and Integration
Costs rise sharply when BI requires building or upgrading a data warehouse, deploying real-time data pipelines, or integrating legacy systems. While cloud-native tools can reduce infrastructure overhead, integration is often one of the most labor- and resource-intensive parts of the project.
Insight: Basic integration projects typically start at around $80,000, but multi-source orchestration can increase costs to over $200,000. (ScienceSoft, 2024)
Implementation and Advisory Services
Third-party BI implementation consultants and system integrators typically add 20–50% to the overall costs of a BI implementation project plan. While this may seem high, these investments often accelerate delivery, reduce risk, and fill internal capability gaps, particularly during the early phases of BI adoption.
Insight: Industry reports from Gartner and McKinsey consistently show that advisory services can account for 15–40% of total transformation spend, with BI often on the higher end due to integration complexity.
User Training and Change Management
BI platforms may be powerful, but without proper onboarding and role-specific training, adoption stalls. Leading BI programs allocate 10–20% of total budgets to enablement, covering everything from live workshops and knowledge bases to internal champions and feedback loops.
Insight: Frameworks like the “10-20-70” model reinforce that technology alone drives only a small part of success; people and process deliver the long-term return.
Security and Data Privacy in BI Implementation
As business intelligence systems become more deeply integrated across departments, they also become stewards of highly sensitive data: financials, customer records, supply chain insights, and more. A modern BI implementation strategy must treat security and data privacy not as secondary considerations, but as central design principles from the outset. Here’s how this can be done:
- Role-Based Access and Governance: Implementing role-based access controls (RBAC) ensures that users only see data relevant to their assigned roles. This reduces risk, reinforces compliance, and avoids unnecessary exposure of sensitive metrics.
- Encryption and Data Protection: All data, whether in motion or at rest, should be encrypted using industry-standard protocols. Most cloud BI tools offer built-in encryption; however, hybrid setups may require additional safeguards.
- Vendor Security Matters: Select BI vendors with robust security credentials (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2) and well-defined breach response plans. This is especially critical when embedding third-party analytics or integrating external data sources.
- Continuous Risk Management: BI systems evolve, new users, new data, new dashboards. Ongoing monitoring, audits, and escalation paths are necessary to keep up with shifting risks and ensure long-term resilience.
When Business Intelligence Isn’t the Right Solution
Business intelligence delivers powerful results when used in the proper context, but it isn’t a fit for every situation. Knowing when to pause or redirect your BI ambitions can prevent wasted resources and allow teams to focus on what matters.
Lack of Execution, Not Insight
If teams already know what needs to be done but struggle with follow-through, BI won’t fix the problem. Dashboards add value when decisions are data-driven, not when the real issue is operational inertia.
Unreliable or Fragmented Data
BI is only as strong as the data behind it. If core systems are disjointed, definitions are inconsistent, or quality issues persist, implementing BI too soon can create noise instead of clarity. In these cases, improving the data foundation should be the primary focus.
Short-Term or Experimental Use Cases
For initiatives like pilot launches or early-stage product testing, flexibility often matters more than formal reporting. BI tools may be too rigid or heavy-handed for projects where inputs shift daily and success is still being defined.
Low Complexity or Organizational Scale
In small teams with limited data and straightforward operations, BI might be overengineered. When a spreadsheet or built-in CRM dashboard can answer key questions, a complete BI stack may not justify the cost or effort.
Not every decision needs a dashboard. Sometimes, the most innovative BI strategy is knowing when to wait until the foundation, scale, and use case truly necessitate it.
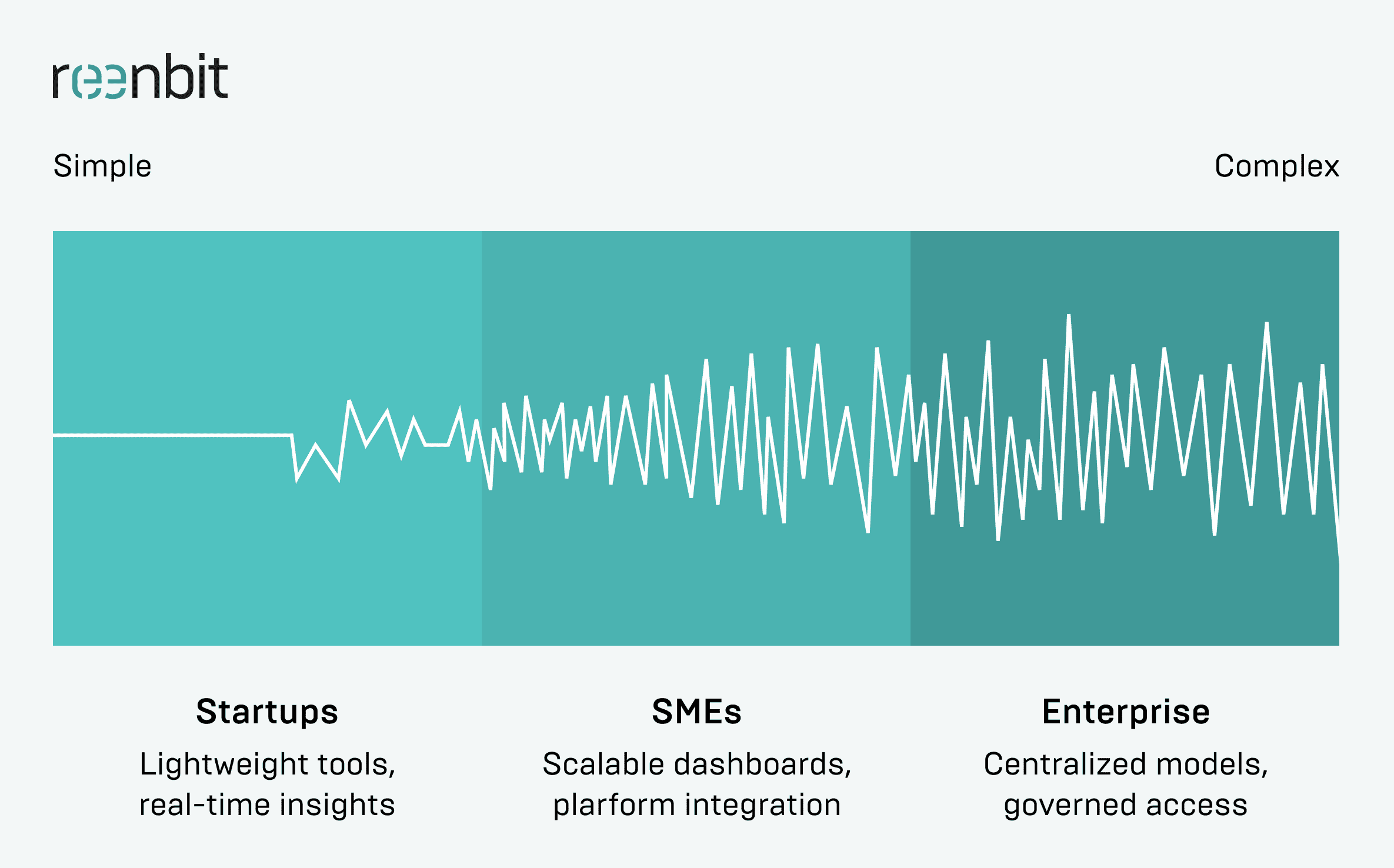
How BI Implementation Differs for Startups, SMEs, and Enterprises?
While business intelligence adds value at every stage of growth, the way it’s implemented and what it must deliver changes dramatically with scale.
Startups
- Focus on: Self-service dashboards, fast setup, real-time visibility
- Risk: Overengineering before reaching data maturity
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
SMEs often find themselves in a transitional stage, handling larger volumes of data across multiple teams and platforms, but without fully matured BI departments. Their challenge is to bring consistency to reporting while keeping workflows agile and resource-efficient.
- Focus on: Scalable dashboards, platform integration, entry-level governance
- Risk: Fragmented ownership and stretched internal capabilities
Enterprises
For large organizations, BI must support complex operations, strict governance, and widespread adoption. The priority shifts to embedding intelligence across departments while maintaining data quality, security, and usability at scale.
- Focus on: Centralized data models, governed access, self-service enablement
- Risk: Siloed implementations, slow adoption, and overcomplexity
Business Intelligence Implementation Case Studies
Successful BI implementation is never just about dashboards; it’s about solving real operational pain and turning data into informed decisions. Below are two examples that illustrate what’s possible when the right tools are combined with the right strategy.
Optimizing Sales Performance Tracking with Power BI
A scaling IT services firm struggled with fragmented sales data across CRMs and spreadsheets, making forecasting unreliable. Reenbit implemented a unified Power BI model, aligning KPIs and creating role-specific dashboards for leadership and regional teams.
Results:
- 70% reduction in sales reporting time
- Improved forecast accuracy across regions
- Enabled strategic territory planning
- Read the full case study here
How the Retail Industry Uses Business Intelligence for Growth
A growing retail chain lacked visibility across eCommerce, POS, and loyalty systems, leaving leadership with outdated reports and inventory issues. By unifying data into a centralized BI platform, Reenbit enabled real-time dashboards for sales, customer behavior, and inventory insights.
Results:
- 30% faster decisions with live analytics
- 73% improved inventory accuracy
- 8.4% sales growth in 12 months
- Read the full article here
BI works when it solves real business problems, not just visualizes data. The most effective implementations are those tied directly to margin, efficiency, and execution.
Conclusion
Effective BI connects technology with strategy, enabling timely insights and confident decisions across the business. With the right goals, tools, and personnel in place, companies can develop scalable systems that drive meaningful impact. Reenbit’s Business intelligence services help make that happen, turning scattered data into clarity, speed, and momentum.
Ready to unlock smarter decisions with BI? Talk to Reenbit today.
FAQ
Why do companies implement BI solutions?
To turn raw data into actionable insights. BI improves decision-making, boosts efficiency, tracks KPIs, and reveals growth opportunities.
Who can implement a business intelligence system?
In-house IT teams, external consultants, or a hybrid. Cloud BI tools also enable smaller teams to deploy without heavy infrastructure.
What tools are commonly used in BI projects?
Popular tools include Power BI, Tableau, Looker, Snowflake, BigQuery, and SSIS. ETL tools and AI features are often used depending on needs.
How do I choose the right BI platform for my business?
Consider your goals, data sources, user needs, scalability, and security. Ease of use, integration, and vendor support are also key.
What departments benefit most from BI implementation?
BI delivers value across the board, but five departments benefit most:
BI adds the most value in:
- Finance – for forecasting, budgeting, and performance tracking
- Marketing – to measure campaign ROI and customer behavior
- Sales – for pipeline visibility and revenue tracking
- Operations – to monitor efficiency and resource use
- Executives – for strategic planning and real-time insights
How do I measure the success of a BI implementation?
Track time saved, dashboard usage, data-driven decisions, improved KPIs, and faster response to business changes.