12 Common Cloud Engineering Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Cloud computing has become a central fixture of the modern business environment. And its popularity is on the rise as more companies recognize the benefits in terms of scalability, cost-efficiency, security, and flexibility. According to Google Cloud, “41.4% of global tech and business leaders plan to increase their investment in cloud-based services and products due to the current economic climate.” Meanwhile, Gartner reports that over 50% of enterprises will utilize cloud tools to leverage their business operations by 2027.
Nowadays, nearly all software applications offer cloud support, empowering users to store data and perform intricate tasks that may exceed the capabilities of their internal storage systems. Consequently, organizations can concentrate on expanding their market presence while relying on cloud computing services for other operational needs.
However, as cloud systems grow more advanced and complex, particular challenges must be addressed to ensure the cloud remains viable for a broader range of businesses. In this blog post, we have outlined the foremost cloud computing challenges in 2023 and beyond and brought solutions to resolve them effectively. Let’s start!
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to providing diverse hardware and software services through remote servers over the Internet. These servers actively store, manage, and process data, enabling users to enhance and expand their infrastructure while accessing files on demand.
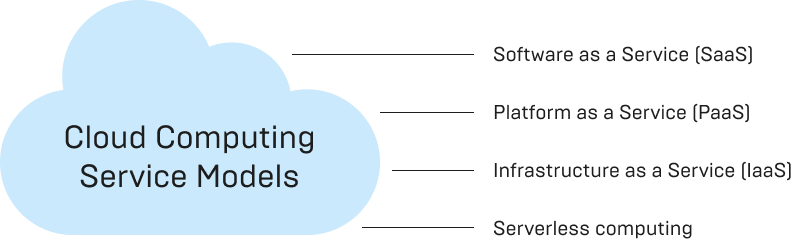
The potential and scope of the cloud are immense. To better understand its applications, the IT industry has categorized three main types of cloud computing:
Software as a Service (SaaS)
That entails the ownership, delivery, and remote management of software by one or more providers. SaaS has gained significant popularity as it offers an alternative approach to accessing and paying for software. Instead of installing the latter on local servers, SaaS companies allow users to rent hosted software for a monthly or yearly subscription fee.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Providers own, and host compute resources, storage, and networking capabilities available to customers on-demand.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
That encompasses various application infrastructure services, including middleware. These services include application platforms, integration tools, business process management solutions, and database services.
These advancements mark a departure from traditional on-premise computing, which relies on local servers or personal computers and is gradually becoming obsolete.
Who Utilizes the Cloud and Why?
Some popular companies have already transitioned to cloud environments, while others are in the process or on the way to doing so.
Here are some notable organizations that have embraced cloud technologies:
- Netflix required a scalable infrastructure to manage its extensive customer base and data. By leveraging cloud computing resources, they efficiently moved the data and improved streaming capabilities for their large user community.
- Due to its rapid growth and millions of user requests, eBay turned to cloud solutions for scalability and enhanced performance. They moved to the Google Cloud Platform in five months with the help of the engineering team.Besides, eBay is considering using Google’s cloud services in different locations worldwide.
- As one of the leading smartwatch manufacturers, Fitbit also relies on cloud resources to enhance user experience and become more attractive to a broad audience. They use Google Cloud for healthcare and life sciences, which enables users to share critical health information with their healthcare providers.
Ultimately, the mentioned organizations have set an example for others, showing the value of cloud storage in facilitating business development.
Cloud Computing Advantages
Cloud service providers have brought about a significant shift in how organizations perceive and utilize IT resources. Businesses opt for public clouds or private clouds since they are:
Scalable
Cloud computing offers elastic scalability, allowing organizations to access the right amount of IT resources precisely when and where they are needed.
Reliable
Cloud providers simplify data backup and disaster recovery, ensuring optimized, cost-effective solutions.
Secure
Using innovative technologies requires a comprehensive suite of cloud policies and controls to enhance overall security, safeguarding data, applications, and infrastructure resources from potential threats.
Fast
Cloud services enable swift deployment of services and resources, often within seconds, granting businesses greater flexibility and agility.
Cost-efficient
Cloud migration projects eliminate significant upfront investments in hardware, software, and server infrastructure, resulting in overall cost savings.
Virtualized
Virtualization and cloud computing are closely intertwined. The first simplifies cost management in the cloud, leading to further cost-cutting measures.
These are just a few of the advantages cloud vendors offer. However, it is essential to note that while these benefits can be achieved, organizations must also manage various cloud computing problems. In the next section, we will explore these challenges in detail.
The Challenges of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has emerged as a discussed topic, raising questions about effectively managing its features and resources. With the continuous advancement of tech, businesses increasingly utilize the latest cloud frameworks as they scale up. That is because cloud solutions offer numerous advantages. However, despite their benefits, such solutions have their challenges. Here, we explore some critical obstacles to embracing cloud computing.
Information Security & Privacy
When working with cloud environments, safeguarding data is a significant issue. Information security poses one of the most considerable cloud computing challenges since users are responsible for their data, and not all cloud providers can guarantee absolute data privacy. Cloud privacy breaches often occur due to a lack of visibility and control tools, the absence of identity access management, data misuse, and misconfiguration of cloud settings.
How to address: Configure network hardware and set up the latest software updates to mitigate potential security vulnerabilities. Employing firewalls and antivirus software and enhancing bandwidth to ensure data availability can also prevent security risks.
Utilization of Multi-Cloud Environments
Challenges associated with managing a multi-cloud strategy include configuration errors, inadequate security patches, data governance shortcomings, and lack of granularity. After all, effectively monitoring security requirements and implementing data management policies across multiple platforms can be daunting.
How to address: Adopt a multi-cloud data management solution as a starting point. But not all tools provide specialized security functionalities, especially considering multi-cloud environments’ ever-increasing sophistication and complexity.
Performance Issues
The effectiveness of cloud solutions relies heavily on the providers offering relevant services to their clients. So, if a cloud vendor experiences a sudden outage, it can significantly impact the business. That represents one of the primary challenges of cloud computing.
How to address: Select vendors that implement proactive real-time SaaS monitoring standards.
Interoperability & Flexibility
Moving applications between different cloud ecosystems poses one of the biggest cloud computing challenges in terms of interoperability. For instance, some fundamental difficulties faced include:
- Adapting app stacks to meet the specifications of the target cloud environment.
- Ensuring seamless data encryption throughout the migration process.
- Establishing operational networks within the target cloud.
- Effectively managing applications and services within the target cloud ecosystem.
How to address: Establish cloud interoperability and portability policies to address these issues in cloud computing before initiating projects. Additionally, multi-layer authentication and authorization tools are highly recommended to verify accounts within public, private, and hybrid cloud ecosystems.
Heavy Reliance on Network
Transferring large amounts of data to and from cloud servers often encounters one of the most common challenges in cloud computing: insufficient network bandwidth. Besides, the data vulnerability increases and the risk of unexpected disruptions becomes a concern.
How to address: Use a two-pronged strategic approach. Firstly, invest in higher bandwidth options. Secondly, focus on enhancing operational efficiency to minimize the dependence on network capabilities.
Insufficient Knowledge & Expert Skills
Companies are grappling with the daunting task of recruiting the most suitable cloud talent. And the need for those possessing the required qualifications is evident. Since workloads continue escalating and the market witnesses a surge in introducing new tools, businesses need experts to navigate them effectively.
How to address: Employ professionals who specialize in DevOps and cloud engineering.
Reliability & Availability
The particular services’ scarcity and unreliability are tremendous challenges of cloud computing. Thus, companies must seek additional resources to meet evolving business needs. But when a cloud vendor is hacked or affected, the critical user data becomes compromised, adding to the numerous security issues and risks the cloud industry faces.
How to address: Implement the NIST Framework standards in your cloud environment.
Ineffective Cost Management
Cloud vendors provide a subscription model where you pay for the services used. However, these costs can accumulate over time. For example, hidden costs arise when businesses fail to utilize their resources fully.
How to address: Regularly audit systems and use resource utilization monitoring tools. That allows for managing budgets efficiently and tackling the key challenges of cloud computing.
Lack of Control & Governance
Effective IT governance ensures the utilization of appropriate tools and the implementation of assets following established procedures and agreed-upon policies. But one of the most prevalent challenges of cloud computing is the need for more governance. That leads companies to employ tools not aligned with their overarching vision. Consequently, IT teams need more control over compliance, risk management, and data quality verification.
How to address: Adapt traditional IT processes to accommodate cloud migration, which allows for seamlessly integrating existing practices with evolving technology.
Data Migration
Migrating data to the сloud can be time-consuming, and not all organizations are adequately prepared. Some encounter challenges such as prolonged downtimes, security concerns, and data formatting and conversions difficulties. Cloud migration projects often become more expensive and challenging than initially anticipated.
How to address: Organizations must allocate resources to hire in-house professionals specializing in cloud data migration. These experts should thoroughly analyze the issues and solutions related to cloud computing before investing in CSPs’ latest platforms and services.
Hybrid-Cloud Complication
Hybrid-cloud complication means difficulties managing computing, storage, and services when using a mix of private cloud services, public clouds, and on-premises infrastructures. And the diverse security challenges further compound such complexity.
How to address: The most effective strategies include implementing centralized cloud management solutions, enhancing automation, and strengthening security measures.
Cloud Integration
Lastly, many companies, particularly those operating in hybrid cloud environments, need help integrating their on-premise applications and tools with public cloud services. This challenge will likely be around for a while since combining modern cloud-based apps with existing legacy systems requires a significant allocation of resources, expertise, and time.
How to address: Explore integration solutions that facilitate seamless communication between on-premise and cloud-based systems. They include adopting middleware techs, API management platforms, or specialized integration tools.
The Future of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become ubiquitous, offering many different services and capabilities. But, as time progresses, cloud service providers will streamline their offerings to focus on core functions. Moreover, leading companies such as Microsoft, Amazon, and Google have played a crucial role in shaping the definition of cloud computing, and they will continue to do so in the future.
The only limitation would be the speed of the internet. It is only possible to envision a future for the IT industry with a fast network speed, as it is the backbone. Thus, it is undeniable that network speed will surpass the current standards, and consequently, all aspects of cloud computing will seamlessly align.
Conclusion
To wrap up, despite the discussed cloud computing challenges, it is one of the most valuable tech resources. This tech continues to revolutionize the landscape of business intelligence (BI), and its adoption rate is projected to increase significantly.
Considering the rapid pace at which information is generated worldwide, companies often need help managing and analyzing it for their purposes effectively. Traditional approaches have become obsolete, as cloud computing effortlessly handles complex data, resolves data storage issues, and automates data interpretation. While challenges persist, adopting a strategic approach and leveraging the expertise of your IT team can guarantee maximum benefits that outweigh cloud computing issues.
Are you seeking to consolidate your cloud services and leverage their scalability, high speed, and cost-efficiency? Unlock the full potential of cloud computing for your business with Reenbit as a reliable and trusted partner and experience seamless integration, excellent support, and a tailored approach to meet your needs. Contact us today and embark on a transformative cloud journey that sets your business apart from competitors.
FAQ
What are cloud computing risks and challenges?
Modern businesses may face multiple cloud computing issues and risks. For instance, the most widespread ones involve information security, multi-cloud environments, inappropriate performance, interoperability, strict compliance policies, insufficient expertise, etc.
What is the biggest problem with the cloud?
The most significant problem is typically cloud security and privacy concerns. Thus, while offering numerous advantages, cloud environments also introduce certain security-related risks, including data breaches, data loss, lack of control, compliance, and legal issues.
Who should not use cloud computing?
The frequent scenarios when the cloud is not a perfect choice for organizations are everyday Internet connection, power outages, and work with compassionate personal data. Also, there is a need to mention the disability to track cloud performance and a lack of understanding related to complex cloud architecture.